Anatomy
Trabecular bone (inner part of the bone) is more affected than cortical bone (outer part of the bone). Spinal vertebrae are usually affected first. Typically, these are the lower thoracic and upper lumbar (T6-L1). If lesions are higher than this, neoplasm must be considered. Thoracic vertebrae (chest level spinal bone) sustain wedge-shaped fractures, while crush fractures are common in lumbar vertebrae.
The post Osteoporosis appeared first on Rehab Experts.
]]>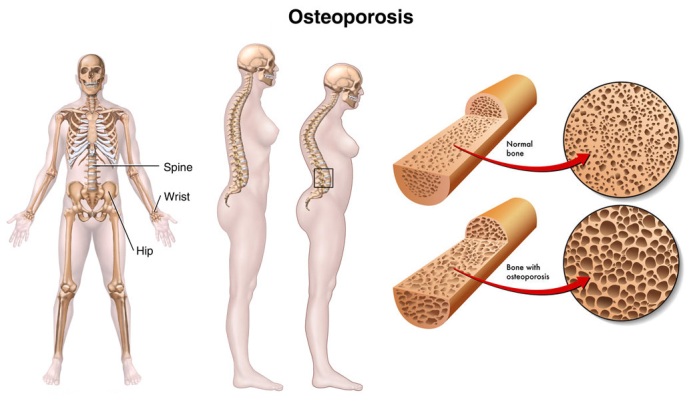
Anatomy
Trabecular bone (inner part of the bone) is more affected than cortical bone (outer part of the bone). Spinal vertebrae are usually affected first. Typically, these are the lower thoracic and upper lumbar (T6-L1). If lesions are higher than this, neoplasm must be considered. Thoracic vertebrae (chest level spinal bone) sustain wedge-shaped fractures, while crush fractures are common in lumbar vertebrae.
Thoracic wedge fractures create the typical “dowager’s hump” of kyphoscoliosis (backward and lateral curvature of the spine). The arms and legs lose their normal proportion to the axial skeleton and appear to be longer. Loss of height due to vertebral collapse may be as much as 5 to 8 inches. This phenomenon may progress until the lower rib cage rests upon the anterior iliac crest.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
- Fair-skinned, white female
- Positive family history
- Thin, small-framed
- Surgical removal of ovaries/early menopause
- Over age 35
- Smoking
- Alcohol ingestion
- High-protein diet
- Sedentary lifestyle
The Scientific Study Of The Nature Of Disease and Its Causes, Processes, Development, And Consequences.
Normally, 10 to 30 % of the skeleton is remodeled yearly by the process of bone mineralization.
Reduced bone mineralization is ubiquitous with age. Until early adulthood, more bone is built than absorbed. By the fourth decade, both males and females experience a gradual loss of bon. However, after menopause, females are 6 times more affected than males. Women lose 0.5% to 1 % of their peak bone mass yearly for approximately 20 years after menopause. The rate of bone loss slows after the age of 65 years.
Estrogen protects against bone loss by reducing plasma calcium, thereby stimulating parathyroid hormone(PTH). This increase the formation of 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol through the kidneys, and thus increases the tubular reabsorption of calcium and intestinal calcium. In this way calcium is maintained in plasma.
An adequate dietary intake of calcium may contribute to osteoporosis. Premenopausal calcium needs are considered to be 800 to 1000 mg/day, while postmenopausal needs 1200 to 1500 mg/day. Secondary hyperparathyroidism may result from reduced absorption or increased excretion of calcium. Vitamin D deficiency also is a factor.
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels increase when dietary calcium is deficient, calcium absorption is defective, or estrogen is absent. PTH maintains constant calcium plasma levels by depleting skeletal stores.
Assessment
Routine radiographic evaluation is not helpful in the detection of osteoporosis, because bone loss must exceed 30% before it becomes apparent. Bone mass measurement may be accomplished through the use of photon absorptionmetry, which measures low energy gamma rays of radionuclide through bone. Single photon absortionmetry is used to evaluate the wrist or heel (cortical bone). Dual photon absorptionmetry (DPA) is used for spinal vertebrae assessment. Ultrasound of the patella has been shown to measure a property of bone fragility that is distinct from bone mass; it is less expensive than DPA but is not widely utilized. CT scanning using a phantom device for comparison is more appropriate, but has drawbacks of expense, radiation exposure, and availability. There is as yet no standard for bone mass measurement, and little to be gained by obtaining routine lateral X-rays of the thoracic and lumbar spine.
Diagnosis is usually made on symptoms of gradual or sudden onset backache and/or change in bodily habitus. It may take up to 4 weeks for an acute compression fracture to become apparent on routine X-ray. It is important that a timely diagnosis be made, so that bone trauma and resultant pain can be minimized, family members at risk can be followed, and other causes of bone loss such as osteomalacia can be eliminated.
Rehabilitative Mangement
Chronic back pain may result from compression fractures or kyphotic/scoliotic changes. Posture can be addressed by several means. A Posture Training Support (PTS) may be used to improve posture in an effort to prevent or lessen osteoporotic skeletal problems. For more involved cases, a back support device can be used, such as a semi-rigid dorsolumbar support with shoulder straps, or a custom-made jacket. Proper back exercises emphasize extension and omit flexion maneuvers. Chonicpain management techniques may be helpful.
Acute back pain secondary to osteoporotic vertebral fracture follows a typical course.
Severe kyphotic posture causes fatigue easily due to ligamentous stretch and reduced vital capacity. A back support device should be worn. Stooping should be discouraged. Chest expansion may be improved by deep breathing exercises, pectoral stretching, and thoracic spine extension.
[tagline_box link=”http://morningcodes.com/rehab/contact-us” linktarget=”” button=”Contact us now!” title=”Physical Therapy Home Service” description=”Are you a person suffering from some physical disabilities? Do you intend to find a solution to your physical disabilities? Are you already tired masking the pain and intend to find a solution to your physical disabilities? Do you intend to address the root-cause of pain and find a lasting remedy to your physical disabilities? Are you looking for a good quality physical therapy home service?”][/tagline_box]
The post Osteoporosis appeared first on Rehab Experts.
]]>The post Concussions & Repeated Minor Head Traumas appeared first on Rehab Experts.
]]>The effects of concussions have rightfully been the focus of an increasing amount of press over the last several years. Some stories are particularly disturbing: the motor deficits seen with boxer Muhammed Ali, incidences of suicides and depression suffered by professional and college level football players.

Head trauma is a very serious issue. Athletes are bigger, quicker, and hit harder than they did decades ago. This likely corresponds with an increase in diagnosed concussions in professional and amateur sports. Recent research, however, is bringing to light something startling about concussions: many athletes are suffering brain damage not only from hard hits, but also from repeated smaller “micro-traumas” to the head.
Micro-traumas to the brain can be seen with something as innocuous as heading a soccer ball, or a football lineman pushing up against a opponent when the ball is snapped. If these activities are repeated over and over again, the end result can be just as disturbing as a diagnosed concussion.
From a rehabilitation standpoint, head injury patients are among the most difficult to treat. Chronic headaches, neck pain, and shooting pain down the arms are very common chronic conditions that arise from head and neck trauma. “Myofascial pain”, or pain stemming from the muscle, nerves, and other soft tissue structures is a common occurrence as well. Behavioral differences are noted when brain tissue is repeatedly knocked against the skull: depression, aggression, and changes in motor speech function are a few examples.
Young athletes often fail to recognize that multiple minor head traumas can have terrible long term consequences. My advice to parents may sound excessive, but is it truly worth a few years of competition and fun for your child, given what we now know about head trauma?
[tagline_box link=”http://morningcodes.com/rehab/contact-us” linktarget=”” button=”Contact us now!” title=”Physical Therapy Home Service” description=”Are you a person suffering from some physical disabilities? Do you intend to find a solution to your physical disabilities? Are you already tired masking the pain and intend to find a solution to your physical disabilities? Do you intend to address the root-cause of pain and find a lasting remedy to your physical disabilities? Are you looking for a good quality physical therapy home service?”][/tagline_box]
Resources:
[one_half last=”no”]
[/one_half]
The post Concussions & Repeated Minor Head Traumas appeared first on Rehab Experts.
]]>